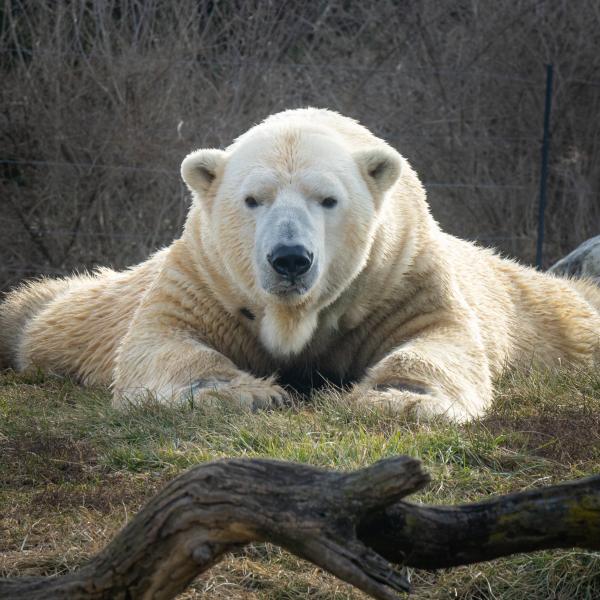
The polar bear inhabits Arctic sea ice, water, islands and continental coastlines.
It prefers sea ice habitat with leads, next to continental coastlines or islands. Leads are water channels or cracks through ice, which may remain open (ice free) for only a few minutes to several months, depending upon weather conditions and water currents. Polar bears hunt seals in the leads, using sea ice as a platform.Â
Scientific Name: Ursus maritimus
Conservation Status: Vulnerable
Size: Height: Male 8 to 10 feet, female 6 to 8 feet
Weight: Male 775 to 1500 lbs., female 350 to 550 lbs.